“Anything can change, because the smartphone revolution is still in the early stages”, Tim Cook.
Smartphones are the mobile phones for this generation that have multi-purpose mobile computing capabilities. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, which facilitate wider software, internet (including web browsing[1] over mobile broadband), and multimedia functionality (including music, video, cameras, and gaming), alongside core phone functions such as voice calls and text messaging.
Let us rewind a little bit…
The earliest of the smartphone dates to the early 1990’s. Frank Canova built a prototype called Angler in 1992, and a refined version was commercially introduced by BellSouth in 1994 under the name Simon Personal Communicator. In addition to placing and receiving cellular calls, the touchscreen-equipped Simon could send and receive faxes and emails. It included an address book, calendar, appointment scheduler, calculator, world time clock, and notepad, as well as other visionary mobile applications such as maps, stock reports and news. But the phone was commercially unsuccessful due to the bulky handset with a limited battery life.
The term “smartphone” was coined in 1995. People who were used to carry a mobile phone and a separate PDA, benefited with the integration of both through the advances in mobile operating systems. These bulky smartphones combined with their high cost and expensive data plans, plus other drawbacks such as expansion limitations and decreased battery life compared to separate standalone devices, generally limited their popularity to “early adopters” and business users who needed portable connectivity. Manufacturers competed in reducing the size of devices.
Japan took the lead in the smartphone market, due to the introduction of i-mode a mobile internet platform by the local wireless provider NTT DoCoMo, that worked well for smartphones. The company had gained 40 million subscribers by the end of 2001 and was ranked first in Japan, and second globally in terms on market cap. The manufacturers built smartphones specifically keeping in mind the Japanese user, as the local demand was quite high they ignored the export market.
The New Age Smartphones
The rise of 3G technology globally and non-Japanese phones with powerful standardized smartphone operating systems, app stores, and advanced wireless network capabilities allowed non-Japanese phone manufacturers to finally break in to the Japanese market, adopting Japanese phone features like emojis, mobile payments, NFC, etc. and introducing them to the rest of the world. Microsoft’s Windows mobile and Blackberry smartphones took the lead in the American markets, and Nokia took lead in the European market. Smartphones then came with a stylus to use on the screen or with a qwerty keypad to enter data.
The first touchscreen phone was launched by LG in 2006 in collaboration with Italian Luxury Designer Prada. Apple Computers forayed into the smartphone market in 2007 with the introduction of the iPhone. Google developed the Android Mobile operating system and launched its first device the HTC Dream in 2008. iPhone and Android smartphones with touch screen form factors made sure the decline of keyboard based smartphones. Although attempts were made by other mobile manufactures to compete with the iPhones and Androids, they failed to capture any significant market share, making the two companies maintain a duopoly in the smartphones market.
Smartphone Adoption
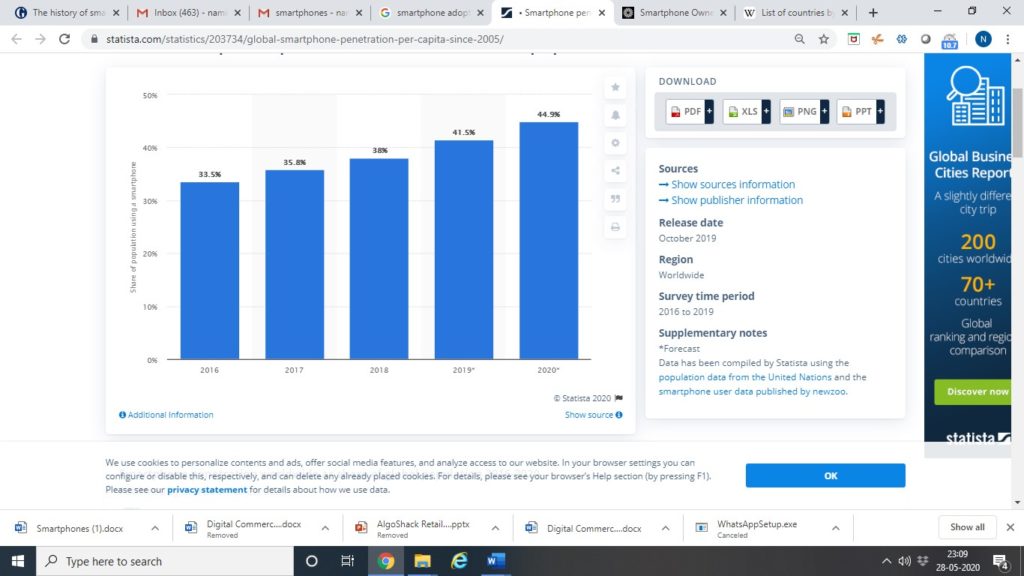
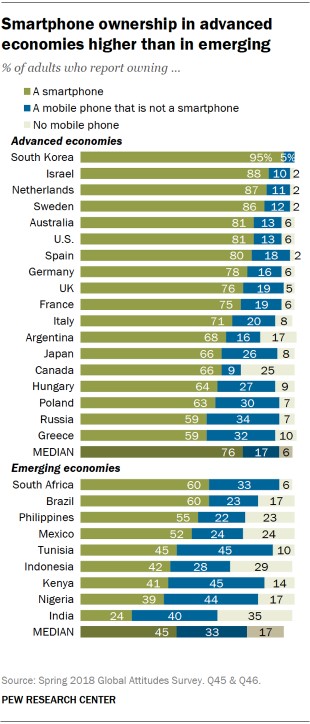
Out of the estimated 5 billion people that use a mobile phone 50% of these are smartphone users. The advanced economies have a larger smartphone user base than the emerging economies. Amongst both the advanced and emerging economies the trend of smartphone usage is high amongst youngsters, than the elderly population. However over the last couple of years the smartphone adoption rate by the elderly demographic has increased steadily, to illustrate, if 5 in 10 people in the 50+ age category used smartphones earlier, now it has increased to 7 in 10 people in that category.
Global smartphone penetration rate as share of population from 2016 to 2020
The Smartphone Entrepreneurship
Whilst much can be argued in terms of the boon and the bane of the role smartphones are playing in everyone’s lives, here’s some positives for entrepreneurs who choose to take advantage of the smartphone infrastructure and systems.
Ease of Starting up
In the pre-smartphone days, to start or launch a business required looking for an appropriate location, finalizing the lease agreement, getting the interiors done, hiring staff, putting systems in place, managing the store etc. Now, the startup world has got much simpler and faster. One just needs to develop a website and/or an app and it is good to go. Consumers these days are drawn to the technological world of what phones have to offer and reaching these consumers had become far quicker than before. If one is not technologically qualified to develop their online presence themselves, no need to worry, there are dozens of well known website and app development companies that can assist in developing, launching and maintaining the website and/or app for customers to visit via their smartphones.
Accessibility
A physical store is limited by operating hours whereas via the website or app the store is open to take orders anytime of the day or night. A physical store is limited to the customers in a given geography, whereas a webstore can expect a customer order from any corner of the world and can execute it. The smartphones enable a global marketplace for entrepreneurs to be able to promote their products and services to customers across the world.
Review and Feedback mechanisms
A physical store is limited with the customer review and feedback to a given geography and demographic. Besides a customer who does shop in a physical store has to rely on personal experience or listen to the staff’s opinion in terms of review for a particular product or brand. But with the smartphone, entrepreneurs can expect customer reviews and feedback from different corners of the world and make it easy for prospective customers to learn real experiences through the reviews posted and make a decision to purchase.
Data Bank
Again, a physical store is limited to local data, but digital stores helps collect diverse set of data. Besides access to data being easier, entrepreneurs are used to getting ideas in unthinkable places at which time a handy smartphone is the best place to record, store or save that relevant idea or information. Access to subjects of interests to entrepreneurs by simply browsing through relevant search results on google, following relevant pages or people on Facebook, Instagram and Twitter.
Virtual Office and Location Free
Smartphones help businesses to operate virtually, as there are a number of resourceful apps that make it easy for teams to connect and work productively. Entrepreneurs can work from anywhere with their smartphone, customers can conveniently order anything from anywhere on their smartphone. No more boundaries in doing business. More so during a time of crisis such as the Covid-19 pandemic.
Virtual Networking
Entrepreneurs can look up Google, LinkedIn and other platforms to connect with likeminded individuals, companies and events. No stress in organizing a travel or commute to network. With the restrictions on movement of people during times of crisis, a smartphone is surely a boon in helping entrepreneurs continue their networking goals.
Self-Development
Entrepreneurs are constantly involved in learning and upgrading their skills and knowledge around things of their interest. With a smartphone there is a lot of ease in accessing the learning resources anywhere anytime. Listen to a good podcast, read an interesting book, watch motivational videos or write the daily journal on the smartphone.
The Smartphone Addiction
A survey conducted by Deloitte noted that more than 1/3rd of the smartphone uses worldwide check their phones within five minutes of waking up in the morning and almost half the number of users check their smartphones at night before going to bed. Approximately 20 percent of the users check their phones around 50 times in a day. Smartphones have become a fixture of modern day living, whether you are riding or driving to work, using a public transport, at a restaurant or café, traveling by air, road or rail, waiting to board or waiting for an arrival at the ports, or simply out for a walk, you can find people glued to their smartphones.
References
Smartphone Ownership Growing Across the World
Global Mobile Consumer Trends – Deloitte
How smartphones have changed entrepreneurism